Angular Momentum and Its Conservation
Angular Momentum and Its Conservation: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Angular Impulse, Angular Impulse with Constant Torque, Angular Momentum, Angular Momentum and Angular Velocity, Angular Momentum of Particle about a Fixed Point, etc.
Important Questions on Angular Momentum and Its Conservation
A planet of mass is in an elliptical orbit about the sun with an orbital period . If be the area of orbit, then its angular momentum would be
An object of mass is projected from ground, with initial velocity , making angle with the horizontal. Find its angular momentum about the point of projection when the object is at its maximum height. (Take )
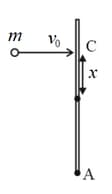
A uniform rod of length and mass is lying on a smooth table. A small particle of mass strikes the rod with velocity at point at a distance from the centre . The particle comes to rest after collision. If the value of , so that the point of the rod remains stationary just after the collision, is, then find .
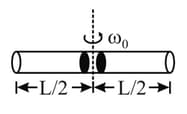
As shown in the figure, two balls of same mass are situated at the centre of a tube of mass and are rotating with a uniform angular velocity If the balls suddenly come to end of the tube the resultant angular velocity will be :
Under the influence of the Coulomb field of charge a charge is moving around it in an elliptical orbit. Find out the correct statement.
A particle of mass starts from rest at from a point and gets accelerated at along in plane. The angular momentum of the particle about the origin (in SI units ) at is
Assertion : The net momentum of a system of two moving particles is zero. Then at a particular instant of time, the net angular momentum of system of given two particle is same about any point.
Reason : If net momentum of a system of two moving particle is zero, then angular momentum of system of given two particles is zero about any point.
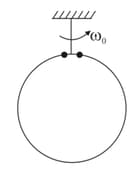
A thin circular ring of mass and radius is rotating about its axis with a constant angular velocity Two objects each of mass are attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The ring now rotates with an angular velocity
An object of mass is projected from ground, with initial velocity , making angle with the horizontal. Find its angular momentum about the point of projection when the object is at its maximum height. (Take )
A rigid metallic sphere is spinning around its own axis in the absence of external torque. If the temperature is raised, its volume increases by . The change in its angular speed is
A ball of mass is thrown directly upward from axis from position. The initial speed of the ball is The magnitude (absolute value) of the angular momentum of the ball about the origin when the ball is halfway back to the ground is:
An object of mass is moving with a uniform velocity of parallel to the direction. At the time of s the particle is located on the axis meters away from the origin then the angular momentum (in ) about at is
If net torque acting on a system is zero, then
A larger ring of mass and two small rings of mass start rotating with angular velocity from the position as shown in figure. Initially small rings are close to axis. There is no friction at any contact surface. Then as time passes. (Consider the motion of small rings till they move up to the bottom most point)
A thin and circular disc of mass and radius is rotating in a horizontal plane about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane with an angular velocity If the another disc of same dimensions but of mass M/4 is placed gently on the first disc co-axially, then the new angular velocity of the system is:-
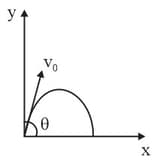
A small particle of mass is projected at an angle with the axis with an initial velocity in the x-y plane as shown in the figure. At a time , the angular momentum of the particle is
Which physical quantity is represented by the product of linear momentum and distance?
The moment of momentum is called
A uniform rod of mass and length is at rest on a smooth horizontal surface. An impulse is applied to the end . The time taken by the rod to turn through a right angle is
If frictional force is neglected and girl bends her hand, then (initially girl is rotating on chair)